a further step in reducing the impact of today and tomorrow
Our goal is set for 2025: to reduce the environmental impact of all Atlantis-branded products compared to current versions.
Our goal is set for 2025: to reduce the environmental impact of all Atlantis-branded products compared to current versions.
But how are carbon dioxide emissions distributed across all the phases analyzed?
The stages of the product life cycle analyzed below are: Upstream (sourcing and processing of raw materials), Core (assembly), Downstream (arrival of goods to Atlantis warehouse).
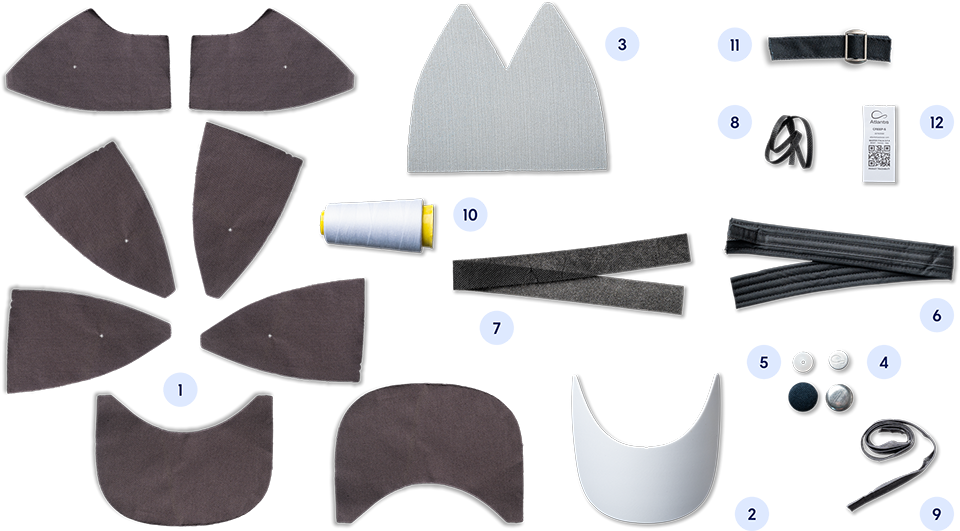
Based on this data, we looked at the incidence of each component in the total emissions of the raw material production, in order to identify those that needed to be addressed as a priority. The result was that yarn and fabric had the highest incidence, followed by the visor, which also contributed to the weight of the hat.
In this way, it was possible to identify the priority elements on which to intervene in order to reduce the impact of the products, especially the more complex ones such as baseball caps.